Measuring the Impacts of Water Safety Plans in the Asia-Pacific Region Kumpel, E., Delaire, C., Peletz, R., Kisiangani, J., Rinehold, A., De France, J., Sutherland, D. and Khush, R. (2018)
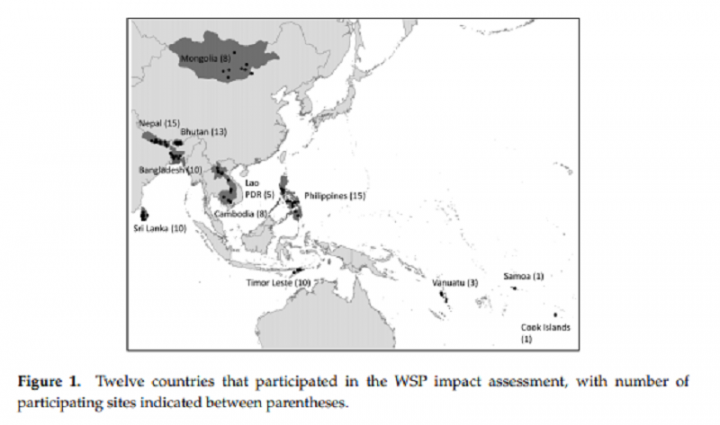
This study investigated the effectiveness of Water Safety Plans (WSP) implemented in 99 water supply systems across 12 countries in the Asia-Pacific region. An impact assessment methodology including 36 indicators was developed based on a conceptual framework proposed by the Center for Disease Control (CDC) and before/after data were collected between November 2014 and June 2016. WSPs were associated with infrastructure improvements at the vast majority (82) of participating sites and to increased financial support at 37 sites. In addition, significant changes were observed in operations and management practices, number of water safety-related meetings, unaccounted-for water, water quality testing activities, and monitoring of consumer satisfaction.
However, the study also revealed challenges in the implementation of WSPs, including financial constraints and
nsufficient capacity. Finally, this study provided an opportunity to test the impact assessment methodology itself, and a series of recommendations are made to improve the approach (indicators, study design, data collection methods) for evaluating WSPs.
Bibliographic information
Kumpel, E., Delaire, C., Peletz, R., Kisiangani, J., Rinehold, A., De France, J., Sutherland, D. and Khush, R. (2018). Measuring the Impacts of Water Safety Plans in the Asia-Pacific Region Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15(6), 1223; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15061223
Filter / Tags
RuralUrban (entire city)
External links
Downloads
Published in: 2018
Pages: 18
Publisher:
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15(6), 1223; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15061223
Author(s):
Kumpel, E., Delaire, C., Peletz, R., Kisiangani, J., Rinehold, A., De France, J., Sutherland, D. and Khush, R.
Uploaded by:
Aquaya
Aquaya Institute
Location of library entry:
